Knee Ligament Surgeon Near Chhindwara
Knee ligaments, resilient connective tissues, stabilize the knee by linking bones and regulating movement. Injuries to vital ligaments on ACL, PCL, MCL,& LCL from trauma or sports may necessitate surgery. Dr. Nawaid Ahmed, an Arthroscopy & Joint Replacement Specialist provides the best treatment for Knee Ligament injuries.
Dr.Nawaid Ahmed
Arthroscopy & Joint Replacement Specialist
Qualification
-MBBS (2002),
-Postgraduate DNB (Diplomate Of National Board)
-Orthopaedics, Fellowship Upper Limb Reconstruction At Melbourne, Australia, 2010
Experience
-Over 20 Years Of Experience
-Visiting Consultant At:
-Alexis Hospital
-Arihant Hospital
-Care Hospital
-KIMS Kingsway Hospital
-Synergy Hospital
Related Treatment
-Knee Cartilage Injury Treatment
-Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Treatment
-ACL Reconstruction Revision Treatment
-Articular Cartilage Treatment
-Ligament injuries Treatment
-Osteoarthritis Treatment & etc.
Contact Us
Address
Sunshine, Central Avenue Road C.A.road Geetanjali Chowk, opposite Hdfc bank, Nagpur, Maharashtra 440018
How To Reach Dr. Nawaid Ahmed
By Railway Station Chhindwara
By Bus Stand Chhindwara
By Badal Bhoi Tribal Museum
By Devgarh Fort Chhindwara
By Domestic Helipad Chhindwara
By Olympic Stadium, Chhindwara
The Nearest Public Transport Station To Dr Nawaid Ahmed Clinic
Nearby Bus Stop
- Gitanjali Square:
130 meters away from Dr Nawaid Ahmed Clinic - Seva Sadan Bhavan:
350 meters away from Dr Nawaid Ahmed Clinic
Nearby Metro Station
- Dosar Bhawan Metro Station:
350 meters away from Dr Nawaid Ahmed Clinic - Agrasen Metro Station:
600 meters away from Dr Nawaid Ahmed Clinic - Meyo Hospital Metro Station:
550 meters away from Dr Nawaid Ahmed Clinic
What are Knee Ligament Injuries?
Knee ligament injuries are injuries that affect the ligaments in the knee joint. Ligaments are tough, flexible bands of tissue that connect bones, providing stability and support to the joint. The knee joint is particularly prone to ligament injuries due to its complex structure and the forces it undergoes during activities.
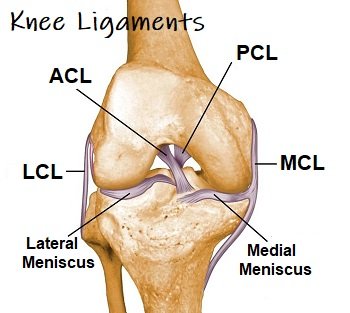
The knee has four main ligaments.
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL): This ligament runs diagonally in the middle of the knee and prevents the tibia (shinbone) from sliding out in front of the femur (thighbone). ACL injuries are common, often occurring during activities involving sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct blows to the knee.
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL): This ligament also runs diagonally in the knee, but it crosses behind the ACL. It helps prevent the tibia from moving too far backward. PCL injuries are less common than ACL injuries and are often the result of direct impact, such as a dashboard injury in a car accident.
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL): This ligament runs along the inner side of the knee and helps stabilize the joint. MCL injuries frequently occur due to a force that pushes the knee outward, often in sports-related incidents.
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL): This ligament runs along the outer side of the knee, providing stability and preventing the knee from moving too far inward. LCL injuries are less common than MCL injuries and typically result from a force pushing the knee inward.
Symptoms of Knee Ligament Injuries
The symptoms of knee ligament injuries can vary depending on the specific ligament involved and the severity of the injury. However, common symptoms often include:
- Pain: Individuals with knee ligament injuries typically experience pain around the affected ligament. The intensity of the pain can vary, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain.
- Swelling: Swelling in the knee joint is a common response to ligament injuries. The injured ligament may cause inflammation in the surrounding tissues, leading to noticeable swelling.
- Instability: Ligaments play a crucial role in stabilizing the knee joint. When a ligament is injured, it can result in a feeling of instability or giving way in the knee. This instability can make it challenging to bear weight on the affected leg.
- Bruising: In some cases, bruising may occur around the knee due to blood vessel damage associated with the injury. The bruising is typically more visible in the days following the injury.
- Limited Range of Motion: Knee ligament injuries can restrict the normal range of motion in the joint. Individuals may find it difficult to fully extend or flex the knee.
- Popping or Snapping Sensation: Some people report hearing or feeling a popping or snapping sensation at the time of the injury. This may be accompanied by immediate pain.
- Tenderness to Touch: The area around the injured ligament may be tender to the touch. Pressing on or around the affected ligament can elicit pain.
Causes of Knee Ligament Injuries
- Sudden Stops or Changes in Direction: Rapid changes in direction or sudden stops, common in sports like soccer, basketball and football, can place excessive stress on the knee ligaments.
- Twisting of the Knee: Twisting motions, especially when the foot is planted and the knee twists in the opposite direction, can lead to ligament injuries.
- Direct Impact: A direct blow to the knee, such as in a car accident or a fall, can cause ligament damage.
- Hyperextension: When the knee is forced to extend beyond its normal range of motion, it can result in injury to the ligaments.
- Landing Incorrectly: Landing from a jump with poor technique or form can contribute to ligament injuries.
Treatments For Knee Ligament Injuries
A - Non-Surgical Treatment For Knee Ligament Injuries
- Rest: Allow the knee to rest to promote healing.
- Ice: Applying ice can help reduce swelling.
- Compression: Compression bandages may be used to control swelling.
- Elevation: Elevating the leg can also help reduce swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve the range of motion.
- Knee Braces: Provide support and stability to the injured knee, especially for MCL and LCL injuries.
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs: Over-the-counter or prescription medications to manage pain and inflammation.
- Intra-articular injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation.
B- Surgical Treatment For Knee Ligament Injuries
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction:
- Procedure: In ACL reconstruction, the torn ligament is replaced with a graft. Common graft options include the patellar tendon, hamstring tendon, or quadriceps tendon.
- Surgery Technique: The surgeon makes small incisions around the knee and uses arthroscopic instruments to perform the procedure.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy is crucial post-surgery to regain strength, stability, and range of motion.
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Reconstruction:
- Procedure: PCL reconstruction involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft, often using the patellar tendon or hamstring tendon.
- Surgery Technique: Similar to ACL reconstruction, PCL reconstruction is usually performed arthroscopically.
- Rehabilitation: Post-operative physical therapy is essential for optimal recovery.
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Repair or Reconstruction:
- Procedure: In some cases, MCL injuries may be managed conservatively with non-surgical methods. However, severe MCL injuries may require surgical repair or reconstruction.
- Surgery Technique: Surgical techniques may involve repairing the torn ligament or using grafts for reconstruction.
- Rehabilitation: Post-surgery rehabilitation focuses on restoring stability and function.
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Repair or Reconstruction:
- Procedure: LCL injuries are less common than MCL injuries. Surgical intervention may involve repairing the damaged ligament or using grafts for reconstruction.
- Surgery Technique: Depending on the severity of the injury, surgical techniques may vary.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy is essential to regain strength and stability after surgery.
- Combined Ligament Reconstructions:
- In some cases, individuals may have multiple ligament injuries. Surgeons may perform combined ligament reconstructions during a single surgery.
- Meniscus Repair or Debridement:
- If there is associated meniscus damage, surgeons may perform meniscus repair or debridement during ligament surgery.
- Arthroscopic Procedures:
- Most ligament surgeries are performed arthroscopically, involving small incisions and the use of a tiny camera (arthroscope) for visualization.
The choice between surgical and non-surgical treatment depends on various factors, including the specific ligament injured, the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. The decision is typically made in consultation with an orthopedic surgeon who will assess the individual case and recommend the most appropriate course of action.
Benefits of Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for knee ligament injuries, particularly when indicated based on the severity of the injury and associated instability, can offer several benefits.
- Restoration of Stability: Surgical procedures, such as ligament reconstruction, aim to restore the stability of the knee joint. This is especially important for injuries to major ligaments like the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) which play a crucial role in stabilizing the knee during various movements.
- Improved Functionality: Surgical treatment can contribute to improved functionality of the knee joint. Reconstruction or repair of damaged ligaments can help individuals regain a greater range of motion and perform daily activities with more ease.
- Prevention of Further Damage: Surgical intervention can prevent further damage to the knee joint. Unaddressed ligament injuries may lead to chronic instability, cartilage damage, and an increased risk of other associated knee problems. Surgery aims to address these issues and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
- Reduced Risk of Secondary Injuries: Knee instability resulting from ligament injuries can contribute to a higher risk of secondary injuries. Surgical treatment helps reduce this risk by restoring stability to the knee, which, in turn, can lower the likelihood of additional injuries, such as meniscal tears or cartilage damage.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: For individuals involved in sports or activities requiring a high level of knee stability and function, surgical treatment can contribute to enhanced athletic performance. Properly reconstructed ligaments can provide the necessary support for demanding physical activities.
- Long-Term Joint Health: Surgical treatment, when successful, can contribute to the long-term health of the knee joint. By addressing ligament injuries and associated issues promptly, individuals may experience improved joint health and a reduced risk of degenerative changes over time.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation: Surgical procedures are often followed by structured rehabilitation programs. Physical therapy and rehabilitation help individuals regain strength, flexibility, and proprioception, leading to a more comprehensive recovery.
Famous Places Near Dr. Nawaid Ahmed's Clinic
Sitabuldi Market
Sitabuldi market in central Nagpur, known as the Heart of the city
Mominpura Market
Mominpura was hailed as the Chandni Chowk of Nagpur
Raman Science Center
It is an interactive science center affiliated with Nehru Science Centre Mumbai.
VR Mall
Stylish retail center offering brand-name fashion stores, homewares, electronics & casual eateries.
