Knee Arthroscopy vs Traditional Surgery: What Is the Difference?
Knee pain is one of the most common orthopaedic complaints among Indians today. Whether it is caused by sports injuries, age-related wear and tear, ligament tears, or accidents, knee problems can severely affect daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, squatting, or even standing for long periods.
When medicines, physiotherapy, or lifestyle changes do not provide relief, surgery may be recommended. But most patients feel confused when doctors mention different surgical options—especially when they hear “arthroscopy” versus “open knee surgery.”
What Is Knee Arthroscopy?
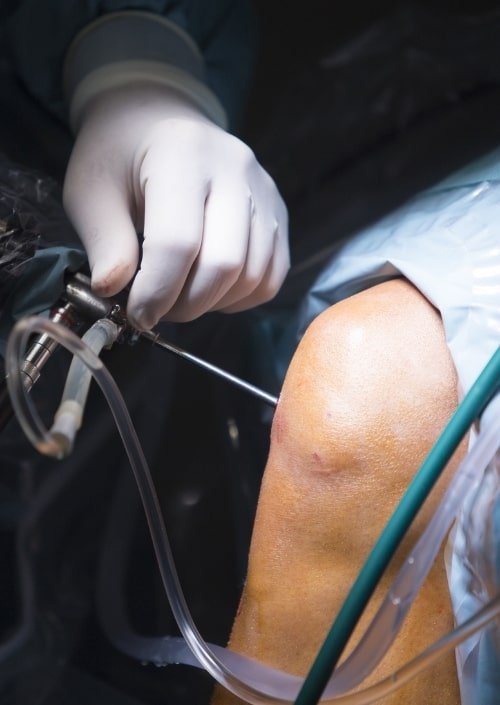
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat various knee joint problems. Instead of making a large incision, the surgeon only creates two or three small keyhole cuts around the knee.
Through one incision, a tiny camera called an arthroscope is inserted. It projects high-definition images onto a screen, allowing the surgeon to see inside the knee joint clearly. Through the other keyhole incisions, miniature surgical instruments are inserted to repair the damaged tissues.
Common conditions treated with knee arthroscopy:
- Torn meniscus
- ACL or PCL ligament injuries
- Loose bone fragments
- Cartilage damage
- Inflamed synovial tissue
- Patella issues
- Removal of cysts or debris
Why is arthroscopy preferred today?
Because it is less invasive, less painful, and offers faster recovery, especially for sports injuries and early-stage knee damage.

What Is Traditional Knee Surgery (Open Surgery)?

Traditional knee surgery, often called open surgery, involves making a large incision, usually 8–10 cm or more, to directly access the knee joint. This method provides the surgeon a wide open view of the knee structures.
Traditional knee surgery is required for:
- Severe fractures
- Complex ligament injuries
- Advanced osteoarthritis
- Knee replacements
- Tumour removal
- Major cartilage reconstruction
- Multi-ligament injuries
Though open surgery takes longer to heal, it is still considered the gold standard for complex or advanced knee conditions where minimally invasive techniques may not be enough.
Knee Arthroscopy vs Traditional Surgery: A Detailed Comparison
Let’s break down the differences point by point so patients can understand clearly.
A. Surgical Technique
| Arthroscopy | Open Surgery |
| Small keyhole incisions | Larger incision |
| A mini camera guides the surgery | Direct open access to the joint |
| Minimal cutting of muscles and tissues | More tissue disruption |
| Highly precise due to enhanced visualization | Suitable for larger repairs |
B. Type of Conditions Treated
| Knee Arthroscopy Best for: | Traditional Surgery Best for: |
| Minor to moderate ligament tears (like ACL reconstruction) | Severe osteoarthritis |
| Meniscus repair or removal | Knee replacement surgeries |
| Cleaning damaged cartilage | Complex fractures |
| Treating inflammation | Major ligament reconstruction |
| Early arthritis treatments | Structural deformity corrections |
C. Operating Time
- Arthroscopy: Usually 30–90 minutes
- Open Surgery: 1–3 hours depending on complexity
Arthroscopy generally takes less time because it involves smaller incisions and minimal tissue handling.
D. Pain Levels After Surgery
- Arthroscopy: Mild to moderate pain; manageable with basic medications
- Open Surgery: More post-operative pain due to larger incisions and deeper tissue involvement
E. Hospital Stay
- Arthroscopy: Often a day-care procedure; patients can go home the same day
- Open Surgery: Usually requires a 2–4 day hospital stay
F. Recovery Time
This is one of the biggest differences.
| Recovery After Knee Arthroscopy | Recovery After Open Surgery |
| Walking with support: 1–2 days | Walking with support: 1–2 weeks |
| Return to desk work: 1 week | Return to work: 4–6 weeks |
| Resume normal activities: 2–4 weeks | Full recovery: 3–6 months |
| Sports: 6–12 weeks (depending on the repair) | Sports activities: 6–12 months |
So, arthroscopy clearly offers a faster return to normal life.
G. Cost Comparison in India
Costs vary depending on city, hospital, and surgeon. Average range:
Knee Arthroscopy Cost
₹45,000 – ₹1,20,000
(depends on whether it is diagnostic or with ligament repair)
Traditional Knee Surgery Cost
₹1,00,000 – ₹3,00,000 or more
(especially for fracture fixation or replacements)
Overall, arthroscopy is usually more affordable than major open surgeries, unless it involves advanced ligament reconstruction.
Advantages of Knee Arthroscopy
- Minimally invasive
- Faster healing
- Less pain
- Smaller scars
- Less bleeding
- Early return to routine
- Same-day discharge
- Lower risk of complications
Because of these benefits, arthroscopy has become the preferred choice for many knee-related problems, especially in young adults and sportspersons.
Advantages of Traditional/Open Knee Surgery
Even though arthroscopy is more modern, open surgery has its own importance.
- Better for complex or severe knee damage
- Necessary for knee replacement
- More effective for major fractures
- Offers wide surgical visibility
- Suitable for advanced arthritis
In short, some cases simply cannot be treated through keyhole surgery and require open access.
Which Procedure Is Better for You?
The answer depends entirely on the type and severity of your knee problem.
Arthroscopy Is Better If You Have:
- Torn meniscus
- ACL or PCL injury
- Cartilage damage
- Loose bodies
- Mild-to-moderate arthritis
- Synovitis
- Sports injuries
Traditional/Open Surgery Is Better If You Have:
- Severe arthritis
- Complex fractures
- Joint deformity
- Major ligament reconstruction needs
- Bracing or fixation required
- Knee replacement requirement
An orthopaedic surgeon will recommend the right procedure after analysing MRI reports, X-rays, physical tests, and overall symptoms.
Recovery Tips After Any Knee Surgery
No matter which procedure you undergo, your recovery largely depends on how well you follow post-surgery instructions.
Important Recovery Guidelines:
- Take medications on time
- Apply ice packs to reduce swelling
- Avoid squatting or sitting cross-legged initially
- Don’t lift heavy weights
- Wear knee braces if advised
- Start physiotherapy early for best results
- Maintain a healthy diet and hydration
- Avoid long-standing activities during the healing phase
Proper physiotherapy plays a major role in ensuring full and smooth recovery.
Knee Arthroscopy vs Open Surgery:
| Feature | Knee Arthroscopy | Traditional/Open Surgery |
| Incision Size | 0.5–1 cm | 8–10 cm or more |
| Pain Level | Mild | Moderate to High |
| Recovery Time | 2–6 weeks | 2–6 months |
| Hospital Stay | Same day discharge | 2–4 days |
| Scarring | Minimal | Significant |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best For | Sports injuries, minor tears | Major fractures, replacements |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | Highly invasive |
Arthroscopy or Traditional Surgery—Which One to Choose?
There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Both procedures have their own strengths, and the choice depends on:
- Your diagnosis
- Level of damage
- Age and lifestyle
- Treatment expectations
- Surgeon’s recommendation
Arthroscopy is ideal for smaller, repairable issues with a quick recovery.
Traditional surgery is essential for complex, chronic, or severe knee damage where arthroscopy alone is not enough.
If you want the best outcome, consult an experienced orthopaedic surgeon who can evaluate your reports and suggest the safest and most effective option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Which is better — knee arthroscopy or open surgery?
It depends on your knee condition. Arthroscopy is better for minor to moderate ligament injuries, meniscus tears, cartilage damage, and sports injuries. Open surgery is necessary for severe arthritis, complex fractures, deformities, and knee replacement.
2. Is knee arthroscopy painful?
Arthroscopy involves very small incisions, so patients usually experience only mild to moderate pain after the procedure. Pain is easily managed with basic medications and reduces quickly within a few days.
3. How long does recovery take after knee arthroscopy?
Most patients return to normal activities within 2–4 weeks. Complete healing may take 6–12 weeks, depending on the type of repair and physiotherapy.
4. How long does recovery take after traditional/open knee surgery?
Recovery from open surgery is longer because the incision is larger. Full recovery may take 2–6 months, and sometimes up to a year for major surgeries like ligament reconstruction or knee replacement.
5. Can knee arthroscopy treat arthritis?
Arthroscopy can help in early-stage arthritis to remove loose cartilage or inflamed tissue, but it cannot cure advanced osteoarthritis. Severe arthritis usually requires traditional surgery or knee replacement.
6. Is hospital stay required after knee arthroscopy?
Not usually. Arthroscopy is often performed as a day-care procedure, and most patients go home the same day.
7. Can I walk immediately after knee arthroscopy?
Yes, most patients can walk with support within 1–2 days. However, the amount of weight you can put on your leg depends on the type of repair done.
8. Is arthroscopy safe for elderly patients?
Yes, arthroscopy is considered safe for older adults as long as they do not have severe arthritis or major knee deformities. However, for advanced conditions, open surgery or replacement may be more suitable.
Understanding the differences between knee arthroscopy and traditional open knee surgery helps patients feel more confident and informed about their treatment. Arthroscopy offers faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring, making it the preferred choice for many conditions. However, open surgery remains crucial for severe injuries, advanced arthritis, and complex structural problems.
If you’re experiencing knee pain, locking, swelling, or mobility issues, do not delay consulting an arthroscopy and joint replacement specialist. Early diagnosis and the correct surgical approach can prevent long-term complications and bring you back to an active, pain-free life.